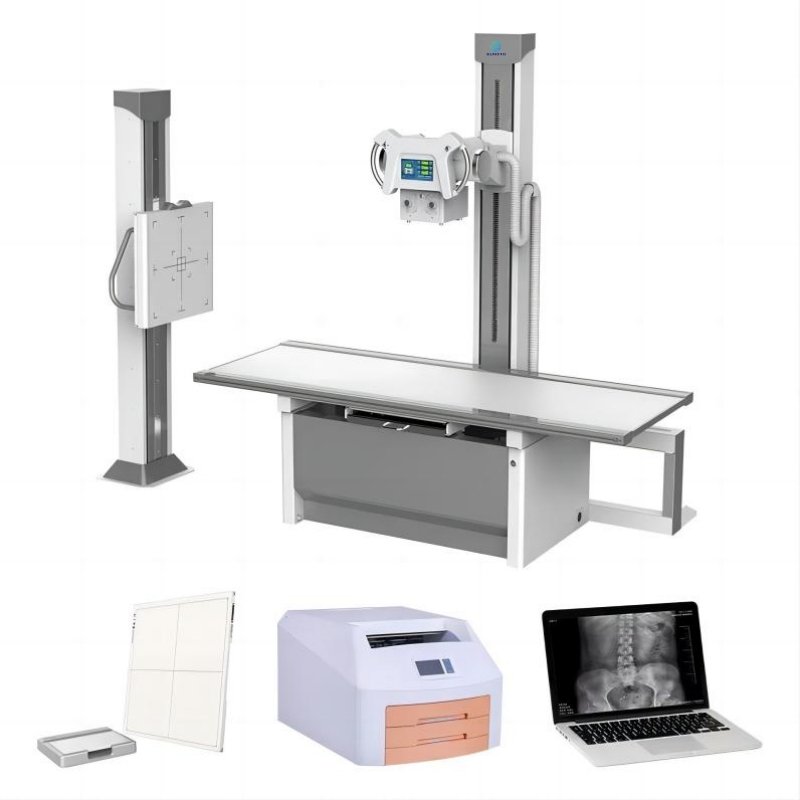
X-Ray_Machine_Guide
A Complete Guide to X-Ray Machines: Principles, Components, Types, and Applications
X-ray machines are one of the most essential and widely used imaging devices in modern medical diagnostics. Whether in hospitals, clinics, or health examination centers, X-ray imaging plays a vital role thanks to its fast imaging speed, low radiation dose, and broad clinical applicability. This article provides a comprehensive introduction to how X-ray machines work, their key components, common types, major applications, and the advantages of digital radiography (DR). It is designed to help healthcare institutions and medical professionals better understand the fundamentals and selection criteria of X-ray systems.
1. How an X-Ray Machine Works
The working principle of an X-ray machine is based on the penetration characteristics of X-rays. When X-rays pass through the human body, different tissues absorb radiation differently due to their varying densities. For example, bones absorb more X-rays and appear white on the image, while soft tissues absorb less, appearing in shades of gray.
The imaging process includes:
– High voltage generation
– X-ray production inside the tube
– X-ray penetration through the body
– Signal detection via film or digital detectors
– Image processing and enhancement
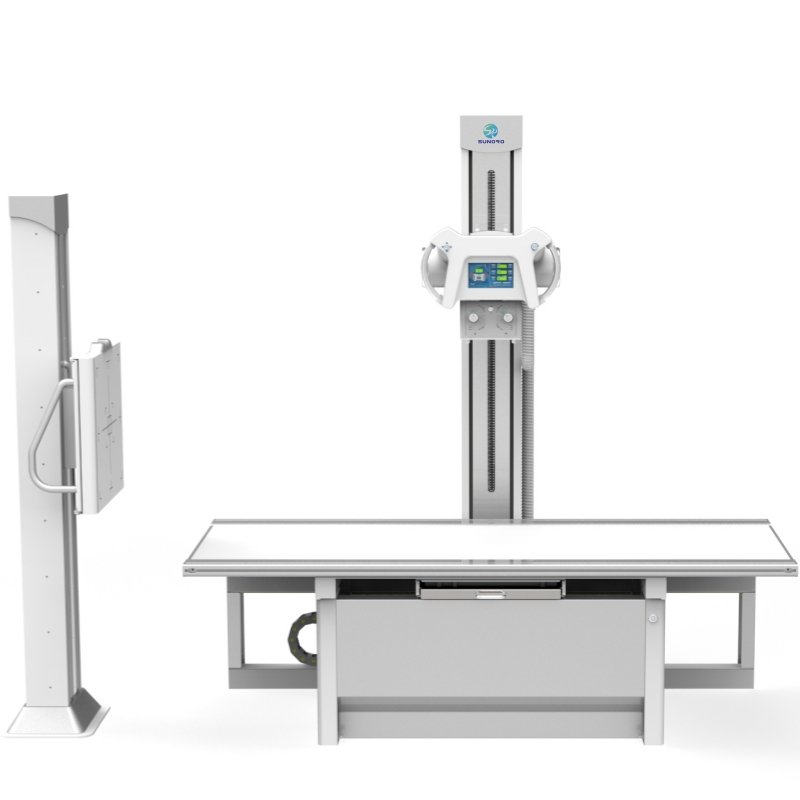
2. Key Components of an X-Ray Machine
– X-ray tube
– High voltage generator
– Flat panel detector (DR)
– Image processing workstation
– Mechanical stand or arm system
3. Common Types of X-Ray Machines
– Standing DR systems
– Mobile X-ray machines
– Bedside portable DR
– Dental X-ray units
– Mammography machines
4. Major Applications
– Bone and joint imaging
– Chest examination
– Abdominal imaging
– Emergency and trauma assessment
– Dental diagnosis
5. Benefits of Digital X-Ray Machines (DR)
– Faster imaging
– Higher image clarity
– Lower radiation dose
– Digital enhancement tools
– Easy archiving and PACS integration
6. Key Factors When Selecting an X-Ray Machine
– Resolution and detector quality
– Wired or wireless DR
– Dose control capability
– Generator stability
– Ergonomic design
– Software compatibility
– After-sales support and maintenance
Conclusion
X-ray machines remain a cornerstone of diagnostic medicine. With advancements in digital radiography, modern X-ray systems offer clearer imaging, faster workflow, and enhanced clinical value. Understanding the technology and selection considerations helps healthcare providers choose the best imaging solutions for long-term use.